Nowadays, there are different ways to build, test, and deploy your applications to your development, testing or production environments. Back in the 90’s, programmers used to just copy a ZIP file, a WAR file, or the binary files in the webapps directory of their monolithic web servers and then manually configure and restart their Apache, NGINX, and IBM WebSphere servers to reflect the changes. The deployment process is quite manual and prone to a lot of errors. A lot of moving parts are done by hand, which may take several hours to complete due to the lack of automation. Moreover, provisioning the required virtual web server or a dedicated database cluster will take you weeks or even months to accomplish due to a lack of automation.
Today, you can do your deployment in a blink of an eye through the various deployment tools available at your disposal via the power of the cloud. Amazon Web Services (AWS) offers a number of services that provide deployment and management capabilities for one or more aspects of your enterprise application lifecycle. These features and services enable organizations to build and deliver applications way faster than their traditional CI/CD workflow counterpart.

Your development team doesn’t have to spend a lot of time manually provisioning, configuring, updating, monitoring, or securing your AWS resources anymore. These laborious tasks can be programmed into code and easily automated with the different deployment services available in the AWS platform.
Some of these services use the concept of “Infrastructure as Code” or IaC, which is a process of managing and provisioning your servers, databases, CDNs, and other resources through machine-readable definition files. You only need to provide a text-based definition file that will automatically provision the required resources for your application in just one click of a button.
The advent of cloud computing enables companies to deploy all their workloads entirely in the public cloud instead of their on-premises data centers. They also have the option to run a hybrid cloud architecture in which they utilize both their physical on-premises resources and cloud services in AWS at the same time. Interestingly, there’s even an option now to do a multi-cloud deployment where you deploy your infrastructure to AWS, Azure, Google Cloud, and other public cloud providers simultaneously. You can run both your multitier applications and Kubernetes or Docker container cluster almost anywhere – whether it be on the cloud, on-premises, on multiple public clouds, or a combination of all three.
Introduction to Amazon EKS and its various Deployment Options
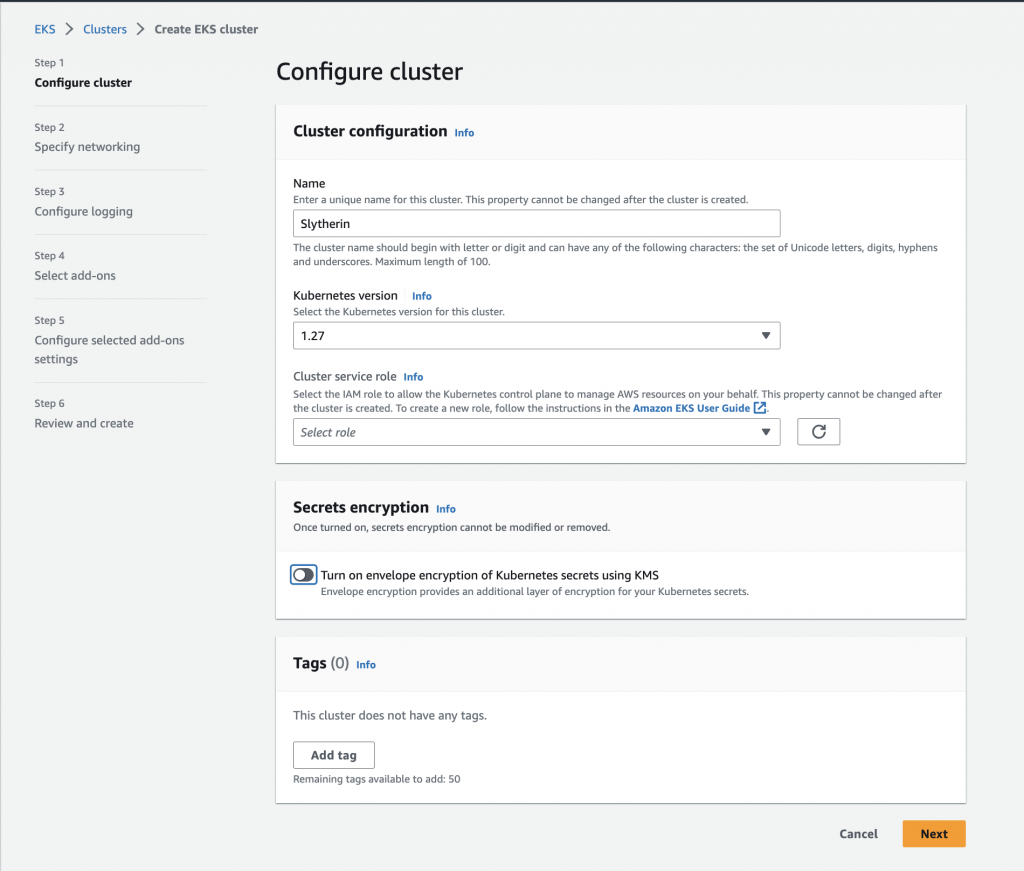
Amazon Elastic Kubernetes Service or Amazon EKS is a managed service that you can use to run Kubernetes on AWS. It’s like Amazon ECS, but instead of Docker containers, this service is used for running Kubernetes clusters. Amazon EKS automates the installation, operation, and maintenance of your own Kubernetes control plane, pods, and nodes.

You can deploy your Kubernetes cluster in various ways in AWS and can include additional networking add-ons to improve your containerized architecture. A Kubernetes container can be deployed to an Amazon EKS cluster in your AWS account, to Amazon EKS on AWS Outposts, to Amazon EKS Anywhere, and through the Amazon EKS Distro. The first option allows you to launch a Kubernetes cluster using managed or self-managed Amazon EC2 nodes that you can customize and control. You can also choose to deploy your Kubernetes pods on AWS Fargate to make the cluster serverless and extremely cost-effective.
The second type is Amazon EKS on AWS Outposts which is a deployment option that uses a physical AWS Outpost rack on your on-premises network to run your Kubernetes workloads. The data plane is also located on-premises, so you can have more control compared with running it exclusively in AWS.
Using Amazon EKS Anywhere is another way to deploy your containers on-premises. It works like Amazon ECS Anywhere, which allows you to run your Kubernetes cluster entirely on your own. This means that the hardware, app deployment location, control plane, and data plane are all controlled on your own physical network. This gives you extensive control over all the components of your containerized application suite while maintaining official support from AWS.
The other deployment option that you can choose is Amazon EKS Distro. The word “distro” simply refers to the distribution of the same open-source Kubernetes software deployed by Amazon EKS in the AWS cloud. Amazon EKS Distro follows the same Kubernetes version release cycle as Amazon EKS and is provided to you as an open-source project that you can deploy on your own computer or on-site environment. It’s similar to the Amazon EKS Anywhere option, except that it does not include support services offered by AWS.